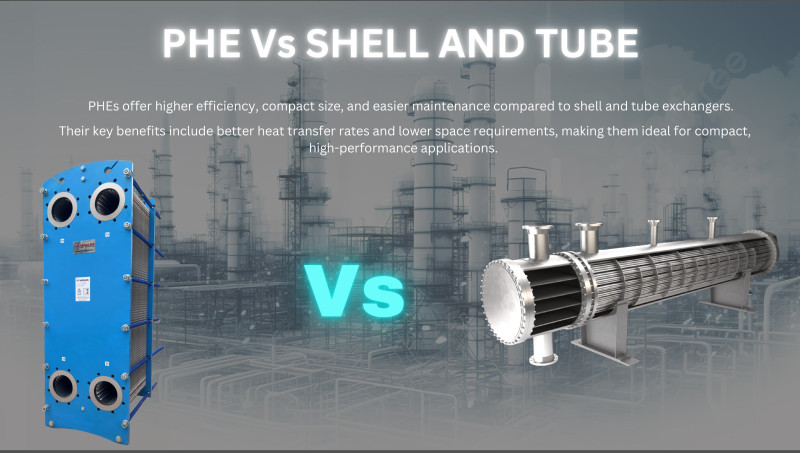
Heat exchangers play a vital role in industries like power generation, HVAC, food processing, and oil & gas. Two popular types are plate type heat exchangers (PHEs) and shell and tube heat exchangers (STHEs). In this blog, we’ll explore their differences, advantages, and limitations to help you choose the right solution for your application.
What is a Plate Heat Exchanger?
A plate heat exchanger uses thin, corrugated plates stacked together to transfer heat between fluids. The plates are arranged in a way that creates alternating channels for hot and cold fluids, enhancing surface area and thermal efficiency.
Advantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
- High efficiency: Greater surface area promotes efficient heat transfer.
- Compact design: Ideal for installations with limited space.
- Easy maintenance: Plates can be easily disassembled and cleaned.
- Scalable: Additional plates can be added to increase capacity.
Disadvantages of Plate Heat Exchangers
- Limited pressure handling: Not suitable for very high-pressure applications.
- Gasket degradation: Gaskets may require frequent replacement in high-temperature environments.
What is a Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger?
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of a bundle of tubes within a cylindrical shell. One fluid flows through the tubes, while the other flows around them, facilitating heat exchange. These are common in industries that demand high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Advantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
- Durability: Can handle high pressures and extreme temperatures.
- Suitable for dirty fluids: Less prone to fouling than PHEs.
- Customization: Available in different configurations for various industrial needs.
Disadvantages of Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
- Bulky design: Requires more space for installation.
- Lower efficiency: Less efficient than plate heat exchangers for small temperature differences.
- Difficult maintenance: Cleaning the tubes can be time-consuming.
Key Differences Between Plate and Shell & Tube Heat Exchangers
| Parameter | Plate Heat Exchanger | Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Compact, plate-based | Cylindrical shell with tubes |
| Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Space Requirements | Requires less space | Requires more space |
| Maintenance | Easy, plates are accessible | Difficult, requires tube cleaning |
| Pressure Handling | Limited to moderate pressures | High-pressure applications |
| Fluid Types | Clean fluids preferred | Suitable for fouling or dirty fluids |
| Cost | Typically lower | Higher upfront cost |
| Scalability | Easy to expand by adding plates | Requires significant modification |
Which Heat Exchanger is Right for Your Application?
Choosing between a plate heat exchanger and a shell & tube heat exchanger depends on your specific needs:
- Use a Plate Heat Exchanger if you need high efficiency, compact design, and easy maintenance for clean fluids.
- Use a Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger for high-pressure environments, dirty fluids, or when durability is a priority.
Conclusion
Both plate type and shell & tube heat exchangers offer distinct advantages. For industries like wind power, which require compact and efficient cooling, plate heat exchangers may be ideal. On the other hand, shell & tube heat exchangers are better suited for oil refineries or chemical plants where durability and high-pressure handling are essential.
Choosing the right heat exchanger will depend on factors like fluid type, temperature range, space availability, and maintenance needs. If you're unsure which type best suits your requirements, our experts can help!
Need Expert Advice on Heat Exchangers?
Contact us today to learn more about our range of heat exchangers designed for various industrial applications!